The following information has been taken from the “FAMILIAL DYSAUTONOMIA” A manual of Comprehensive Care Fith Edition 2009 prepared by The Dysautonomia Center in conjunction with The Dysautonomia Foundation.
There is no one diet appropriate for all children with FD, as they vary in their abilities to eat and their tolerances to particular foods. Some observations have been made, however, in regard to nutritional needs, particular preferences, feeding techniques, common irritants, and foods that are hard to swallow or digest.
Nutritional Goals
A well balanced diet is the goal for anyone regardless of age.
A child with FD has problems with swallowing, chewing and decreased taste sensation that call all interfere with nutritional intake. There is a tendency to avoid liquids, stay with soft foods and to develope food fads, ie picl on particular favorite and want nothing else for a stretch of time.
Parents should follow nutritional guidelines essential for growth and health. In some cases dietary suppliments may be required to mee nutritional goals.
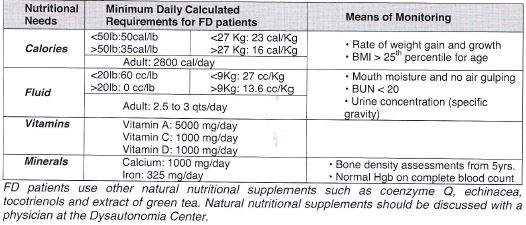
Calories
Children with FD have high metabolic rates. That means that they require the standard calories recommendations. The caroic need for FD patients can be estimatedas 50 calories per pound of body weight (or 23 calories per kilogram of body weight), until the child reaches 50 lbs (23kg); then the caloric requirement decreases to 35 calories per pound (16 calories per kilogram)
A 20lb (9kg) child needs a minimum of 1000 caolries each day.
An 80lb (36kg) adolescent requires 2800 calories a day as a minimum
Fluid
A child with FD has unusually high fluid losses because of the tendancy to drool and or sweat profusely.
Therefore, FD patients have extrordinary high fluid requiremetns. Adewquate hydration is paramount for normal body functions. Signs of thirst in an infant include tounge darker (concentrated) with a stronger small or the child may be constipated. Acute profound dehydration may have deleterious effects on the kidneys. Giving adequate aamounts of fluid is vital throughout an FD childs lfe.
Minimal daily fluid intake is calculated at 60cc (or 2 ounces) per pound (or 0.5kg) of body weight for the child up to 20 pound (9Kg), and 20cc (or 1 ounce) per pound (or 0.5kg) for larger individuals.
If a child is unable to consume enough calories or fluid by mouth because of swallowing difficulties, an alternative intake route must be found. Tube feeding may be necessary to provide a growing child with adequate nutrition and fluid intake.
Tyramine
The charity FDNOW recommend a Tyramine-Safe diet. The Tyramine – free food lsit below is courtesy of FDNOW.
Please note:
- This list was compiled from approximately 20 tyramine lists found on the internet. While similar, no two lists were identical. In fact, most lists conflicted. For example, mozzarella cheese appears in the safe column on most lists, but also appears in the caution column on some lists. This variation is caused by the same food having different amounts of tyramine in it when tested by the list-maker.
- When items appeared in two columns, the item was placed in the more restrictive column. For example, canned shellfish appears in the caution column in most lists, but appears in the avoid column in a few lists. For safety, canned shellfish appears in the avoid column on this list.
- Because the same food may have different amounts of tyramine in it from batch to batch, lot to lot, preparation to preparation, there will not be a fool-proof list.
- In classifying a few items, such as beets and spinach they typically appeared in the safe column however they were placed in either caution or the avoid column due to scientific finding generated by the Laboratory for Familial Dysautonomia Research at Fordham University.
| Food group | Safe | Caution | Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eat as desired | Eat one/day or rarely | Never eat | |
| Contains very little or no tyramine | Conflicting reports | Contains lots of tyramine | |
| Meat, fish, poultry, eggs and other protein sources | all fresh or frozen meat, fish, poultry | canned or fresh tuna | aged, dried, fermented, salted, smoked or pickled |
| beef, lamb, pork, veal, chicken, Cornish hen, turkey, duck, capon, goose | fresh mackerel | processed meats and fish: luncheon meats with nitrates or nitrites, bacon, pepperoni, salami, liverwurst, liver, sausage, bologna, cured ham, hot dogs, corned beef, lox, anchovies, roe, herrings, caviar, sardines | |
| fresh shellfish (clams, lobster, crabs, oysters, scallops, shrimp, squid) | fresh or canned bonito | poultry skin | |
| all eggs | fresh or canned anchovies | meats prepared with tenderizer | |
| Eat the day bought or freeze | canned shellfish (clams, lobster, crabs, oysters, scallops, shrimp, squid) | game meat | |
| canned pilchards | shrimp paste | ||
| Eat the day opened | quiche | ||
| protein dietary supplements w/yeast extracts | |||
| Dairy | milk: skim, 2%, whole, dried, sweetened, condensed, evaporated, eggnog, vanilla milkshake | farmers, Havarti, Boursin | aged cheese spreads, all aged or hard cheese: (bluem feta, brick, brie, cheddar, colby, boursalt, Gouda, gruyere, swiss, roquefort, stilton, provolone, emmentaler, parmesan, muenster, romano, camembert |
| unfermented cheese: cottage cheese, cream cheese, cream, ricotta, American, Velveeta, Cheese Wiz, pasteurized low-fat processed | fresh yogurt, buttermilk, sour cream (4oz) | non pasteurized | |
| part-skim mozzarella (30q) | |||
| Bread, Cereal, Pasta | commercial breads: white, wheat, rye, French, Italian, English muffin, melba toast, crackers, rye crisp, bagel, roll | commercially prepared yeast, plain yeast, leavened products made with baker’s yeast | aged, dried, fermented, salted, all yeast extracts, including brewer’s and yeast paste (marmite) |
| products leavened with baking powder: biscuits, pancakes, coffee cakes | homemade yeast leavened breads and coffee cakes | ||
| hot and cold cereal: cream of wheat, oatmeal, corn flakes, puffed wheat, rice, all bran | sourdough bread | ||
| all pasta: spaghetti, rotini, macaroni and egg noodles | cheese bread | ||
| rice, stuffing | |||
| Vegetables | fresh, frozen, canned: corn, carrots, pumpkin, squash, zucchini, potatoes, cooked onions in food, soy beans | raw onion | snow peas, fava or broad or lima beans, sauerkraut, pickles and olives, avocado, tofu, eggplant, broccoli, beets, spinach, asparagus |
| tomatoes | navy beans | ||
| chinese pea pods | |||
| string beans | |||
| Fruits | fresh, frozen, canned: apple applesauce, blonde cherries, apricots, peaches | orange, grapefruit, tangerine, pineapple, lemon, lime (1/2 cup) | fermented or overripe fruit, figs, raisins, banana peel, red plum, prune, red cherries, fruit cake, cranberries, raspberries, preserves |
| Fats | margarine, butter, mayonnaise, salas dressings w/o ages cheese, vegetable oils | peanut butter | dressing with aged cheese, gravies and sauces with meat extracts (marmite) |
| nuts | |||
| Soup/Sauces | homemade | miso | |
| soup cubes or packets | |||
| canned or dry with autolyzed or hydrolyzed yeastm meat extracts, MSG | |||
| soups gravies and stews prepared in large production or commercial use | |||
| soy sauce, teriyaki sauce | |||
| Dessert | sherbet, ice cream, gelatin, sugar, jelly, jam, honey, molasses, candy, cakes, pastries, cookies, pies, custard, pudding, marshmallow | chocolate | mincemeat pie |
| chocolate syrup | cheesecake | ||
| cheese-filled | |||
| imported chocolate | |||
| Beverages | juice, milk, Tang, Koolaide, lemonade, soy milk | carbonated drinks, regular coffee, tea (8oz) | wine, beer |
| acidophilus milk | |||
| Miscellaneous | natural potato chips, popcorn, syrup, white and brown sugar, jelly, salt, pepper, spices, mustard, vanilla, herbs, white vinegar, flavorings | nutmeg | |
| ginseng | |||
| Ingredients Listed on Food Lables | MSG | ||
| nitrates and nitrites | |||
| yeast extracts, hydrolyzed or autolyzed yeast, meat extracts | |||
| meat tenderizers (papain, bromelin) | |||
| Any foods listed in this column! | |||
| Check for long expiration date | |||
| Leftovers | OK if 1-2 days old. | Discard after 48 hours | |
| Freeze for future. |
